Petrochemicals are chemical products derived from petroleum or natural gas. These products are essential in a wide range of industries, including agriculture, manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, and more. One of the most widely used petrochemical products is urea, a key component in fertilizers that significantly contributes to food production and agricultural productivity worldwide. In this article, we will delve into what urea is, its production process, its applications, and its importance in various industries.
What is Urea?
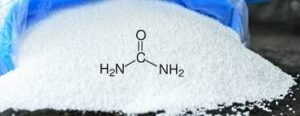
Urea, chemically known as carbamamide, is an organic compound composed of nitrogen, carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen. It has the chemical formula NH₂CONH₂. Urea is the most common nitrogen fertilizer used in agriculture and is also used in the production of various industrial chemicals, plastics, and resins.
It is primarily known for its role in promoting plant growth by providing an easily accessible source of nitrogen, an essential nutrient for plants. As a petrochemical product, urea is typically synthesized from ammonia and carbon dioxide in a highly controlled industrial process.
The Production of Urea
Urea is produced through a process called the Haber-Bosch process, which involves the synthesis of ammonia (NH₃) from nitrogen and hydrogen gases. The steps involved in urea production are as follows:
-
Ammonia Production:
The production of urea begins with the Haber-Bosch process, in which nitrogen (usually obtained from air) and hydrogen (derived from natural gas) are reacted under high temperature and pressure in the presence of a catalyst to produce ammonia gas. -
Reaction with Carbon Dioxide:
Ammonia is then combined with carbon dioxide (CO₂), which is typically captured from the flue gases of power plants or other industrial processes. The reaction forms ammonium carbamate, which is then dehydrated to produce urea. -
Urea Granulation:
After the chemical reaction, urea is in a liquid form. It is then cooled and granulated to form solid urea prills or granules. This process makes it easier to handle and transport for use in agricultural applications.
Applications of Urea
Urea has a wide range of applications, particularly in agriculture, but it is also used in other industries. Here are the key areas where urea plays an essential role:

-
Agriculture – Fertilizers:
Urea is most commonly used as a fertilizer in agricultural applications. It provides a highly concentrated source of nitrogen, which is crucial for the growth of plants. Nitrogen helps plants in the formation of amino acids, proteins, and chlorophyll, promoting healthy leaf and stem development. Urea fertilizers are highly effective in enhancing crop yields, particularly for crops like wheat, rice, maize, and vegetables. -
Animal Feed:
Urea is also used in animal feed to supplement the nitrogen intake of livestock, particularly ruminants like cows and sheep. It helps improve the protein levels in the feed, enhancing the growth and productivity of livestock. -
Industrial Uses:
Apart from fertilizers, urea is used in a variety of industrial applications:- Plastics: Urea is used in the production of urea-formaldehyde resins, which are utilized in manufacturing particleboard, plywood, and other construction materials.
- Pharmaceuticals: Urea is an important component in pharmaceutical formulations, particularly in creams and ointments. It helps in skin moisturization and acts as an exfoliant.
- Adhesives and Coatings: Urea-formaldehyde resins are also used in the production of adhesives and coatings, which are crucial in various industries like automotive and textiles.
-
Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF):
In the automotive industry, urea is used in the Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) technology of diesel engines to reduce nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions. Urea, when mixed with water, forms Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF), which is injected into the exhaust system to help convert harmful pollutants into harmless nitrogen and water vapor. -
Melamine Production:
Urea is a primary raw material in the production of melamine, a compound used in the production of durable, heat-resistant plastics and laminates, often found in kitchenware, furniture, and electrical components.
Importance of Urea in Agriculture and Food Security
Urea plays a significant role in global food production. As a fertilizer, it has become an indispensable tool in increasing agricultural productivity. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), nitrogen fertilizers like urea contribute significantly to enhancing crop yields, helping to meet the growing demand for food as the global population rises.
In regions where arable land is limited, the use of urea fertilizers allows farmers to maximize their crop production per unit of land. However, it is important to note that the excessive use of urea and other nitrogen-based fertilizers can lead to environmental issues such as soil acidification and water contamination. Therefore, proper management and application of fertilizers are essential for sustainable agricultural practices.
Environmental Considerations and Challenges
While urea is highly effective as a fertilizer, its widespread use has raised environmental concerns. When urea is applied in excess, it can lead to nitrogen runoff, which contaminates water bodies and causes eutrophication, resulting in algae blooms and oxygen depletion in aquatic ecosystems. Additionally, the process of producing urea requires a substantial amount of energy, which contributes to carbon emissions.
To mitigate these issues, researchers and industry leaders are developing more sustainable urea fertilizers, such as slow-release urea, which reduces nitrogen leaching and allows for more efficient nutrient use by plants. Innovations in urea production technologies that use less energy and reduce carbon footprints are also being pursued.
Conclusion: Urea’s Role in Modern Industry
Urea is one of the most versatile and essential petrochemical products, with vital applications in agriculture, industry, and even the environment. As the demand for food increases and industries continue to evolve, the production and responsible use of urea will remain a cornerstone of global development. By enhancing crop yields and supporting various industrial processes, urea continues to shape the future of food security, sustainability, and industrial growth.




No Comment