
Rebar is a fundamental material in the construction industry, playing a pivotal role in reinforcing structural integrity. Crafted from steel rods, it stands out for its exceptional strength, which bolsters concrete’s durability and helps prevent cracking or structural failures. Offered in various types and sizes, rebar is adaptable to the diverse needs of civil engineering projects. Without rebar, concrete alone would struggle to withstand tensile forces, leading to considerable structural vulnerabilities. Its incorporation ensures the even distribution of loads across structures. Beyond building construction, rebar finds widespread use in infrastructure projects such as roads, dams, tunnels, and bridges.
Its versatility spanning different shapes and steel grades necessitates careful selection to match project-specific conditions. Additionally, factors like flexibility and corrosion resistance often influence the choice of rebar. Special coatings are sometimes applied to improve resistance to rust in humid environments. These features significantly contribute to maintaining structural durability over time. Advancements in technology have driven production toward higher-quality materials and stricter standards. This progress extends the lifespan of structures and reaffirms the importance of understanding rebar’s benchmarks.
Far from being a mere construction component, rebar is indispensable for safety and longevity. Its robust mechanical properties play a key role in creating resilient infrastructure worldwide. Rigorous quality control remains essential throughout the construction process.
Major Global Rebar Standards
In global markets, diverse standards govern rebar production and quality, ensuring safety and compatibility. A key standard is ASTM, predominantly used in the United States. This defines chemical composition, mechanical properties, and testing procedures for consistent high quality.It aids engineers in selecting appropriate rebar based on required strength and ductility. In the United Kingdom, British Standards (BS) set crucial quality benchmarks. For instance, BS 4449 specifies requirements concerning dimensions, tensile strength, and bendability.
These standards often align with European Norms (EN), promoting trade across Europe. British standards focus on uniformity and traceability in manufacturing. Germany’s DIN standards are renowned for precision and rigor in technical specifications. DIN 488 outlines key characteristics for rebar used in concrete reinforcement. These standards emphasize mechanical properties and chemical composition to guarantee durability. German standards influence both domestic and international markets significantly.
In Asia, Japanese Industrial Standards (JIS) are significant with JIS G3112 as the main guideline. This standard covers yield strength, elongation, and surface conditions comprehensively. JIS embodies Japan’s dedication to precise quality control and innovation. Collectively, ASTM, BS, DIN, and JIS form a global framework supporting trade. They ensure quality and safety of rebar across various international projects effectively.
ASTM Technical Specifications
The ASTM standard provides comprehensive technical specifications addressing chemical composition and mechanical properties. Yield strength, ultimate tensile strength, elongation, and bend requirements are all defined. Rebars are classified into categories like A615, A706, and A955 for specific applications.
For instance, A615 pertains to standard carbon-steel rebars. A706 is designed for weldable rebars known for high ductility. ASTM outlines testing protocols such as tensile tests and bend tests. These evaluate performance under varying load conditions rigorously. Reverse bend tests are also specified to ensure reliability. This flexibility allows U.S. engineers to select optimal grades for seismic zones.
BS 4449 (UK) Technical Specifications
In the United Kingdom, BS 4449 categorizes rebars based on mechanical properties like yield strength. Common yield strength is 500 MPa with specific elongation percentage requirements. Bendability standards ensure structural reliability under stress conditions. It sets guidelines for appearance and marking to ensure straightforward identification. Quality control during construction remains robust through these protocols. The standard advocates uniform rib patterns to improve bonding with concrete. BS 4449 specifies consistent quality control measures during manufacturing. Regular sample testing upholds safety and reliability across all batches. These practices maintain structural integrity in critical UK infrastructure projects.
DIN 488 (Germany) Technical Specifications
Germany’s DIN 488 standard adopts a detailed methodology for assessing rebar. Chemical composition and production techniques receive thorough evaluation. It prioritizes balancing mechanical strength with weldability for industrial projects. Rebars are categorized as B500A, B500B, or B500C with distinct attributes. B500C is characterized by superior bendability and deformation capacity. Rib design optimizes force distribution between steel and concrete. This enhances structural performance significantly under load variations. DIN’s precision guarantees materials perform reliably in extreme stress conditions. German engineering projects depend on this rigorous approach consistently.
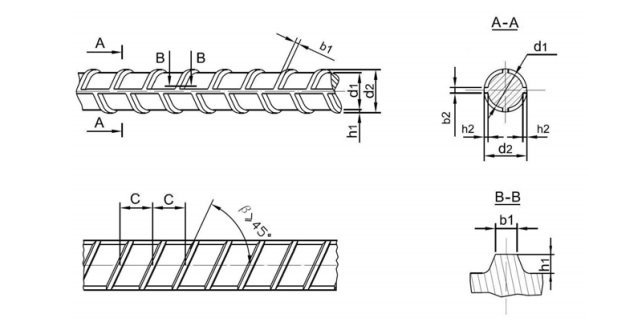
JIS G3112 (Japan) Technical Specifications
The JIS G3112 standard defines precise specifications for rebar comprehensively. Yield strength, ultimate tensile strength, elongation, and surface conditions are covered. Dimensional tolerances ensure exact fit during construction processes. Rebars are labeled as SD295, SD345, or SD390 corresponding to strength levels. JIS emphasizes surface characteristics for improved bonding with concrete. Corrosion resistance receives special attention in material specifications. Rigorous mechanical testing procedures are enforced consistently. Stringent in-plant quality controls maintain production standards. Traceable marking systems enable seamless tracking from mill to site.
This makes JIS ideal for high-sensitivity projects like marine constructions. Precision ensures materials maintain integrity in demanding applications reliably.Click here to view coiled rebar.
Comparative Overview of Rebar Standards
Global rebar standards are all crafted to ensure safety and optimal functionality; however, they exhibit distinct criteria and approaches. In the United States, the ASTM standard prioritizes flexibility and adaptability by offering a variety of rebar types tailored to specific conditions. Alternatively, Germany’s DIN standard emphasizes stricter manufacturing processes and rigorous quality control, aiming for a strong balance between mechanical properties and weldability. Consequently, selecting the most appropriate standard often hinges on the nature of the project and its geographical location. With regard to mechanical properties, BS and DIN standards typically specify higher yield strengths, around 500 MPa, compared to some ASTM grades. Yet, certain ASTM grades, like A706, excel under lateral forces and seismic stress.
Meanwhile, Japan’s JIS standard prioritizes precision, surface quality, and resistance to corrosion, making it especially suitable for projects requiring high accuracy or dealing with demanding environmental conditions. This makes JIS a common choice in industrial and marine constructions. In terms of quality control, European standards such as BS and DIN incorporate sophisticated traceability systems and periodic in-plant testing. ASTM places greater emphasis on field tests and overall performance results. JIS, on the other hand, combines high dimensional accuracy with stringent mechanical testing protocols. These variations empower engineers to select standards that ensure not just quality but also compatibility with locally preferred construction practices.
Regarding labeling and identification of rebar, BS and JIS employ more detailed systems that facilitate seamless tracking from production through installation. ASTM uses a simpler grade-marking system with numeric coding, while DIN includes specific methods for marking rebar surfaces with critical information. Such features are particularly crucial for projects demanding stringent quality checks and precise traceability. Many nations have developed tailored national rebar standards to address their unique climatic, economic, and technical circumstances. While these standards often draw inspiration from international frameworks such as ASTM, BS, DIN, and JIS, they may diverge in aspects like precision, testing protocols, and production techniques.
Their primary aim is to ensure uniformity within local construction practices and establish a legal framework for quality assurance. In Gulf nations such as the UAE and Saudi Arabia, a hybrid approach combining BS and ASTM standards is widely adopted. This ensures compatibility with Western markets while also accommodating regional environmental conditions. Given the scale of construction activities and significant international investments in these countries, stringent quality requirements are imposed on both domestic production and importation of rebar.
Compliance is rigorously monitored through technical certifications and approval mechanisms to uphold structural integrity and reliability. South and Southeast Asian countries such as India, Indonesia, and Malaysia rely heavily on JIS from Japan alongside select influences from ASTM in shaping their national standards.

National Standards and Global Alignment
Many nations develop tailored national rebar standards for unique circumstances. These often draw inspiration from ASTM, BS, DIN, and JIS frameworks. Divergences occur in precision, testing protocols, and production techniques. Their aim is ensuring uniformity within local construction practices. Legal frameworks establish quality assurance mechanisms nationally. In developed countries, harmonization with global standards is consistently pursued. Iran’s ISIRI 3132 integrates elements from DIN and BS benchmarks. Rebars are categorized into types A1, A2, and A3 with distinct properties. Modernization efforts face challenges in testing methodologies and inspections. These inconsistencies pose obstacles to steel product exports internationally. Gulf nations like UAE adopt hybrid BS-ASTM approaches effectively. This ensures compatibility with Western markets and harsh climates.
Stringent quality requirements cover both domestic production and imports. Compliance is monitored through technical certifications rigorously. South Asian countries rely on JIS alongside ASTM influences significantly. Efforts to align with global practices attract foreign investment actively. Variations in manufacturing often necessitate supplementary on-site testing. Harmonization allows standardized materials across multinational projects efficiently. Countries aligning national regulations gain competitive advantages globally. Standard compatibility has reached unprecedented importance recently.

Impact of Standards on the Global Market
International standards shape the global rebar market by setting quality benchmarks. They establish trust among manufacturers, exporters, and consumers reliably. Products become consistent, comparable, and assessable through these frameworks. This enhances transparency and simplifies international trade processes. Without standards, risks of low-quality products increase significantly. Testing costs and material adaptation expenses would rise unnecessarily.
Adhering to standards facilitates rebar export and import efficiently. Countries aligned with global standards gain easier market access. Competitiveness improves while market diversity broadens considerably. Standards enable manufacturers to tailor products for specific markets. Innovation drives market share expansion through quality improvements. Safety and longevity of global structures depend on these benchmarks. Climate variations and load conditions require universal material standards. They reduce structural failures from defects or insufficient load management. Infrastructure integrity remains protected while business reputations stay intact. Standards minimize commercial risks in cross-border transactions effectively. Clear criteria reduce disputes and legal complications substantially. Contract execution and project delivery become streamlined processes.
Investor confidence grows with standardized quality expectations. International companies participate more actively in global markets. Technological advancement accelerates across the entire industry. Manufacturers adopt stricter requirements and upgrade processes continuously. Waste reduction and better environmental practices emerge naturally. High-quality adaptable materials benefit the entire construction sector. Sustainable growth and healthy competition characterize compliant markets. Rigorous safety and performance expectations become industry norms universally.

Challenges, Developments and Conclusion
Adapting standards for new technologies and materials presents major challenges. Special alloy steels require constant revision of existing frameworks. Sustainable manufacturing practices demand updated testing methodologies. Effective collaboration among stakeholders is essential for alignment. Adoption speeds vary significantly across different nations globally. Some update quickly while others lag due to financial barriers. This inconsistency creates quality gaps complicating international trade. Environmental sustainability increasingly influences new standard development. Guidelines focus on reducing energy consumption and emissions actively. Recycled materials usage receives strong encouragement in modern standards. Implementation requires significant investment and comprehensive training programs. Digitalization transforms production and quality control processes fundamentally.

Artificial intelligence and IoT enhance material tracking capabilities. Blockchain enables tamper-proof quality assurance throughout supply chains. These technologies require advanced infrastructure and international cooperation. Global competition demands quicker standard development cycles. Companies must respond swiftly to market and technological changes. Standardization bodies face pressure to expedite drafting processes. Rebar standards maintain structural quality and safety universally. Clear benchmarks ensure reliable materials align with specifications. Without standards, defect risks and incompatibility would increase dramatically. Harmonizing national standards expands global trade opportunities significantly. Manufacturers access broader markets with universally recognized quality. The industry progresses toward sustained growth and healthier competition.
Evolving technologies and environmental demands necessitate constant updates. Robust collaboration among institutions and authorities is crucial. Transparency minimizes commercial risks while fostering investor confidence. Digital transformation enhances traceability through AI and blockchain solutions. Rapid technological advancement demands quicker norm revisions urgently. Staying competitive requires expediting approval processes internationally. Modern standards should encompass environmental and economic considerations. Sustainability goals promote resource-efficient green steel production. Standards form the foundation ensuring safety, quality, and competitiveness globally. Anticipating trends and addressing challenges drives sustainable expansion. International alignment remains vital for success in this key industry. Click here to view coiled rebar.





No Comment