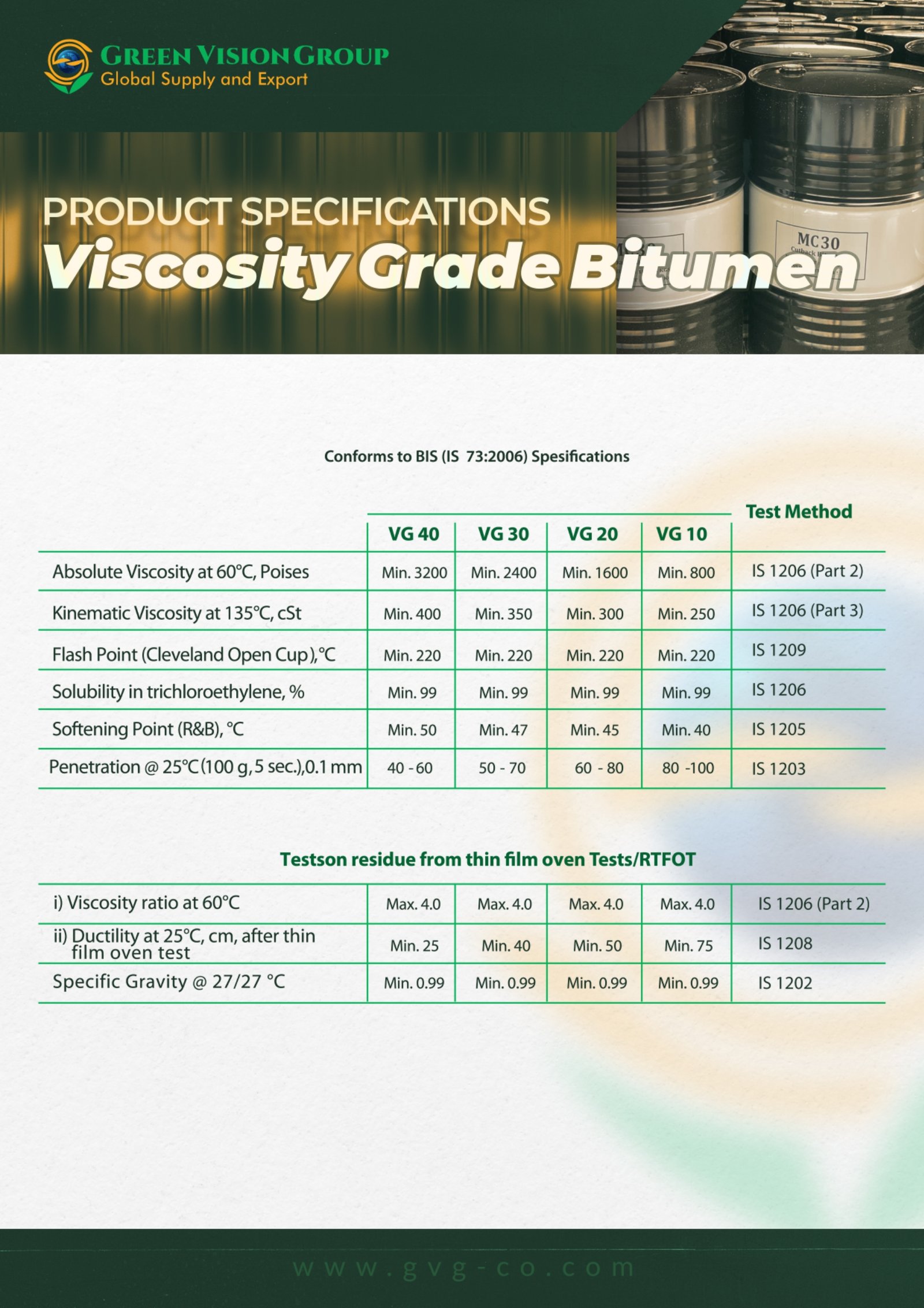
Viscosity Grade Bitumen (VG Bitumen) represents a modern approach to classifying paving bitumen, tailored to deliver reliable performance across varying temperature and traffic conditions. Unlike the traditional Penetration Grade system, which assesses hardness through penetration depth, the VG classification is based on viscosity, or resistance to flow, measured at standardized temperatures. This ensures bitumen behaves predictably under extreme temperatures during both construction and its service life.
According to IS 73:2013 and ASTM D2171, VG Bitumen is divided into four grades:
VG-10, VG-20, VG-30, and VG-40. Each grade corresponds to specific viscosity ranges that determine its suitability for diverse applications, from colder climates to highways experiencing heavy traffic and high temperatures.
VG-10: Best suited for colder regions or high-altitude areas where faster workability is crucial. VG-20: Appropriate for moderate climatic and traffic conditions.
VG-30: The most commonly utilized grade for highways, offering an optimal compromise between stiffness and flexibility.
VG-40: Designed for tropical regions and roads with heavy traffic loads, ensuring enhanced durability and resistance to rutting.
The VG grading system provides engineers with precise control over bitumen selection, resulting in superior pavement quality, minimized rutting, and improved thermal stability. This methodology has gained widespread acceptance in regions like India, the Middle East, and Africa, where temperature fluctuations heavily influence asphalt performance.